Time
After launching the new product, company wants the product to enjoy a long and happy life. However, it does not expect the product to sell forever, the company wants to earn a decent profit to cover all efforts and risks that went into launching it. Marketer is aware that each product will have a life cycle.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a Product Life Cycle?
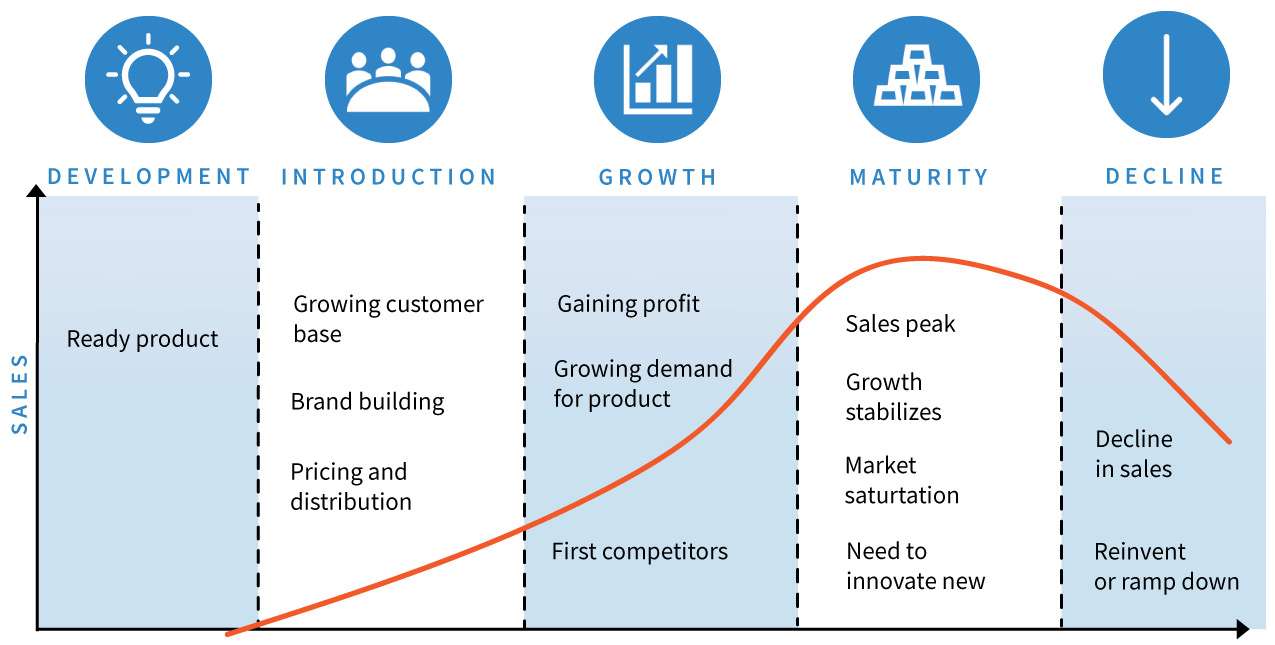
Product Life Cycle is the course of a product’s sales and profits over its lifetime. The phases a product goes through from the time it’s first made available to consumers until it’s taken off the market.
Marketers may use it as a helpful tool to examine and create strategies for their products as they move through each stage and beyond.
Fashion industry trends are short-lived. Fashion week launches new designer collections, which progress to mass production and adoption (growth stage), followed by discounted sales (maturity stage), and finally clearance sales before new trends emerge (decline stage).
- Product development Stage: Prototypes are made and concepts are generated throughout the product development stage. The business finds and develops new product concepts at this time. There are no sales and a bigger investment from the corporation.
- Introduction stage: During the product introduction stage, a company launches its product to the market for the first time. Marketers focuses on creating awareness through advertising and sales promotion. Slow sales growth and profits are expected due to heavy expenses.
- Growth Stage: Growth Stage is a time of quickening market acceptance and rising revenue. where competitors start to appear and demand rises quickly.
- Maturity Stage: In the maturity stage, sales growth slows down as most potential customers have accepted the product. Competition intensifies due to similar products in the market. To maintain market position, businesses employ cost-cutting or differentiation tactics.
- Decline Stage: Decline is when sales and profits decrease for a product due to changing consumer preferences or newer options. Companies may try to extend the product’s life by rebranding or discontinuing it.
Importance of Understanding the Product Life Cycle
Understanding the product life cycle is important for businesses to make informed decisions and successful marketing plans. Conducting a comprehensive analysis of the life cycle, from development to decline, helps predict market trends and adjust strategies accordingly.
Identifying opportunities for new products: By knowing where their current products are in the life cycle, businesses may use the product life cycle to find potential for new products.
For instance, Apple released the iPhone during the iPod’s decline and the iPad after the iPhone matured. Knowing the product life cycle’s stages helps businesses stay ahead and plan
Developing effective marketing strategies: Different marketing techniques are needed for each stage of the product life cycle. During the introduction phase, raise interest and awareness. During the expansion period, increase consumer base size and foster brand loyalty.
To survive the maturity period, companies must retain market share and differentiate their product from competitors. During decline, adjusting pricing or creating new marketing campaigns may help prolong the product’s lifespan.
Managing costs and resources: Businesses can manage expenses and resources by using the product life cycle. Invest in R&D at launch when sales are low. Increase output in growth stage to meet demand.
Additionally, in order to retain profitability at the maturity stage, they might have to reduce expenses and optimize operations. Businesses can decide how best to deploy their resources by knowing where their products are in the life cycle.
Toyota efficiently manages resources and costs using the product life cycle. When the Prius reached maturity, they introduced the more compact and affordable Prius C, retaining and expanding market share
Planning for changes in demand: Throughout a product’s life cycle, demand fluctuates at several points. Businesses must comprehend these shifts in demand to adjust staffing, inventory levels, and production schedules.
Forecasting future sales: Product life cycle analysis helps companies forecast future sales based on past performance. It enables them to adjust manufacturing and marketing plans, and plan for the introduction of new products to replace old ones.
Factors Impacting a Product's Life Cycle
The life cycle of a product can be influenced by various factors that play a crucial role in its success or failure. Here are some factors that can impact a product’s life cycle:
- Competition: Increased competition can shorten a product’s life cycle by reducing demand and sales. For example, Blockbuster’s decline was accelerated by the emergence of streaming services like Netflix
- Technology: Technological advancements can shorten product life, such as film cameras becoming outdated with the advent of digital cameras.
- Consumer preferences: The life cycle of a product can be impacted by shifts in consumer preferences. For instance, the sales of sugary drinks have been limited by the trend towards healthy eating practices.
- Economic conditions: Economic conditions can impact a product’s life cycle by affecting consumer spending. For example, during a recession, consumers may be less likely to purchase luxury items
- Marketing: Effective marketing can extend a product’s life cycle by increasing demand and sales. For example, Apple’s marketing campaigns have helped the company maintain its market share and continue to grow over time 7.
Product's Life Cycle Stages
In this section, we will discuss the product life cycle in more depth.
Product Development Stage
The product development stage is where all the magic happens! It’s when you take an idea and turn it into a tangible product that will meet the needs of your target market.
This stage involves extensive research, brainstorming, and testing to ensure that your product is innovative, unique, and ready to hit the market.
Sales are zero as a product is in the development stage and company investment is higher. During this stage, you’ll work closely with your team to design prototypes, conduct focus groups or beta testing, and make any necessary adjustments based on feedback.
It’s an exciting time filled with creativity and problem-solving as you bring your vision to life. So buckle up and get ready for a thrilling ride through the product development stage!
Introduction Stage
The introduction stage starts when the new product is first launched in the market. It’s a critical time for products because they are new and untested, and consumer awareness is typically low.
You’ll be investing heavily in marketing efforts to get your product noticed by potential customers. Focusing on building brand recognition, designing distribution channels, and establishing your market presence.
To set your product apart from rivals, it’s critical to convey its features, and advantages through promotions and advertising. The idea is to draw interest and attract early adopters who will assist in promoting favorable word-of-mouth about your fantastic offering.
Characteristics of the Introduction Stage
- Low Sales: Sales volumes are usually low during this stage as the product is new and consumers are not yet aware of it.
- High Costs: Costs are high due to research and development, testing, and marketing expenses.
- Limited Competition: There may be little to no competition depending on how novel the product is.
Effective marketing strategies for success in the Introduction Stage include:
- Product Quality and Reliability: Ensuring the product is reliable and of high quality can satisfy customer needs and wants to build a positive reputation.
- Promotion: Intensive promotion is often necessary to build awareness of the new product. Marketers use different platforms such as social media, ads, tv commercials, print and internet.
- Distribution: It’s important to ensure the product is readily available where and when customers want it.
Growth Stage
If the new product satisfies the market. It will enter a growth stage, and sales and customer demand will skyrocket as more people become aware of your product. It’s like watching a small plant grow into a big, beautiful tree!
In this phase, you’ll see competitors entering the market and trying to grab a piece of the pie. But don’t worry – with effective marketing strategies and continuous improvement, you can maintain your competitive edge.
Keep innovating and finding ways to meet customer needs better than anyone else. This will help you stay ahead and continue growing even faster! So buckle up for an exhilarating ride during the growth stage of your product life cycle!
Characteristics of the Growth Stage
- Increased demand: Demand for the product increases rapidly as more people become aware of it. For example, when Tesla introduced its Model S electric car, demand was high due to the car’s innovative features and performance.
- Increased competition: As demand increases, so does competition. New competitors may enter the market, and existing competitors may increase their marketing efforts. For example, when Uber entered the ride-sharing market, it faced competition from established players like Lyft and traditional taxi companies.
- Increased production: To meet the growing demand, companies may need to increase production capacity. For example, when Apple introduced the iPhone, it had to ramp up production to meet demand.
- Increased profitability: As sales increase, companies may see increased profitability due to economies of scale and increased efficiency. For example, when Amazon’s sales increased due to the popularity of its Prime membership program, the company saw increased profitability due to lower shipping costs and higher customer retention.
- Product development: During the growth stage, companies may need to refine their product to meet the needs of their growing customer base. This can involve adding new features or improving existing ones.
Effective marketing strategies for success in the growth stage include:
- Content marketing: Content marketing can be an effective strategy during the growth stage to increase brand awareness and drive sales.
- Social media marketing: Social media marketing can be an effective way to reach a wider audience and build brand awareness.
- Influencer marketing: Influencer marketing can be an effective way to reach a targeted audience and build brand awareness.
- Email marketing: Email marketing can be an effective way to nurture leads and drive sales during the growth stage.
- Paid advertising: Paid advertising can be an effective way to reach a wider audience and drive sales during the growth stage.
Maturity Stage
In maturity stage, sales and revenue growth slow down as the product reaches its peak level of acceptance in the market. It’s like hitting a sweet spot where sales are at their peak! However, it doesn’t mean you can sit back and relax. Competition intensifies, and new players enter the market with similar products.
You need to focus on retaining your loyal customers while also attracting new ones. You might consider expanding into new markets or introducing variations of your product to cater to different customer preferences.
Characteristics of the Maturity Stage
Stable sales: Sales volumes are stable during this stage as the product has reached its peak level of acceptance in the market.
Increased competition: As sales growth slows down, competition increases. New competitors may enter the market, and existing competitors may increase their marketing efforts.
Lower costs: Costs are lower during the maturity stage due to economies of scale and increased efficiency.
Product differentiation: Product differentiation is crucial during the maturity stage to maintain market share. Companies may need to add new features or improve existing ones to differentiate their product from competitors.
Price competition: Price competition is common during the maturity stage as companies try to maintain market share. Companies may need to lower prices to remain competitive.
Effective marketing strategies for success in the maturity stage include:
Product differentiation: Product differentiation is crucial during the maturity stage to maintain market share. Marketers may need to add new features or improve existing ones to differentiate their product from competitors.
Price competition: Price competition is common during the maturity stage as companies try to maintain market share. Companies may need to lower prices to remain competitive.
Promotion: Promotion is important during the maturity stage to maintain brand awareness and drive sales. Marketers may use a variety of marketing tactics to promote their product, such as advertising, public relations, and social media marketing.
Distribution: Ensuring that the product is readily available where and when customers want it. Companies may need to work with retailers and distributors to ensure that the product is stocked and available for purchase.
Product innovation: Product innovation can help companies maintain their market share and continue to grow over time. Add new features or improve existing ones to meet the changing needs of their customers.
Decline Stage
The sale of most product forms and brands eventually dip. The decline stage is an inevitable part of a product’s life cycle. It’s the point when sales start to decrease, and customer interest begins to wane.
But don’t worry, it happens to every product! In this stage, businesses face tough decisions about whether to continue investing in the product or phase it out.
During the decline stage, competition may increase as other products enter the market. This can lead to price wars and intense promotional efforts just to maintain sales. Companies often need to make difficult choices like reducing costs or diversifying their offerings.
Characteristics of the Decline Stage
Decreased demand: Demand for the product decreases as it becomes outdated and less relevant to consumers.
Increased competition: As sales growth slows down, competition increases. New competitors may enter the market, and existing competitors may increase their marketing efforts.
Lower profitability: As sales decrease, profitability decreases due to lower revenue and increased costs.
Product obsolescence: The product becomes obsolete as new products enter the market and replace it.
Limited distribution: Distribution channels may become limited as retailers and distributors stop carrying the product.
Effective marketing strategies in decline stage include:
Product innovation: Product innovation can help companies extend the life of their product by adding new features or improving existing ones. For example, when Apple’s iPod entered the decline stage, the company introduced the iPod Touch, which had new features and improved functionality.
Price reduction: Price reduction can help companies maintain their market share by making the product more affordable and attractive to consumers.
Promotion: Promotion is important during the decline stage to maintain brand awareness and drive sales. Companies may use a variety of marketing tactics to promote their product, such as advertising, public relations, and social media marketing.
Distribution: Ensuring that the product is readily available where and when customers want it is crucial during the decline stage. Companies may need to work with retailers and distributors to ensure that the product is stocked and available for purchase.
Product differentiation: Product differentiation can help companies maintain their market share by making their product stand out from competitors.
Product Life Cycle vs. BCG (Boston Consulting Group) Matrix
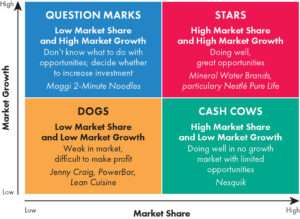
The Product Life Cycle (PLC) and the BCG Matrix are two widely used techniques that marketers frequently use for product analysis and management.
The Product Life Cycle provides a framework for understanding the various stages that a product goes through, from its initial development to its eventual decline.
This framework is based on the analysis of sales volume and profitability over time, which helps marketers to make informed decisions about pricing, promotions, and other marketing efforts at each stage of the product life cycle.
The BCG Matrix categorizes a company’s products into four groups based on their market share and potential for growth. These groups are called stars, question marks (or problem children), cash cows, and dog
The Product Life Cycle and the BCG Matrix work together to provide comprehensive insights into a company’s product strategy.
By combining these frameworks, marketers can identify opportunities for portfolio expansion or reduction. It gains a better understanding of how individual products contribute to overall business objectives.
Summary of PLC characteristics, objectives, and strategies
Characteristics
Introduction
Growth
Maturity
Decline
- Sales
- Costs
- Profit
- Customers
- Competitors
- Product
- Price
- Place (Distribution)
- Promotion
- Low sales
- High Costs
- Profit Negative
- Innovators
- Few
- Offer a baisc product
- use cost-plus
- build selective distribution
- product awarness among early adopters
- Rising sales
- Average Costs
- Rising Profits
- Early adopters
- Growing numbers
- offer product extensions, service,warranty
- penetrate market
- build intensive distribution
- mass market interest
- Peak Sales
- Lower Costs
- High Profits
- Middle majority
- stable number beginning to decline
- Diversify brands and models
- price to match or beat
- more intensive distribution
- stree brand differences and benefits
- Declining Sales
- low Costs
- Declining Profits
- laggards
- Declining number
- terminate weak itemsd
- cut price
- unprofitable outlests
- coverage needed to retain hard core loyals
FAQs
The product life cycle refers to the stages that a product goes through from its introduction to its decline.
The stages of the product life cycle are introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
The product life cycle is important because it helps businesses make informed decisions about advertising budgets, product, prices, distribution channels and packaging.
Product life cycle management is the process of strategizing ways to continuously support and maintain a product.
The introduction stage is the first stage of the product life cycle. During this stage, a company invests heavily in advertising and marketing to make consumers aware of the new product or services
The growth stage is the second stage of the product life cycle. During this stage, sales and revenue increase rapidly as the product gains wider acceptance in the market.
The maturity stage is the third stage of the product life cycle. During this stage, sales and revenue growth slow down as the product reaches its peak level of acceptance in the market.
Pricing is an important consideration during all stages of the product life cycle. Companies may need to set a high price during the introduction stage to recoup their research and development costs, or they may need to set a low price during the growth stage to encourage customers to try the product.
Characteristics of the introduction stage include low sales, high costs, and limited competition.
Effective marketing strategies during the introduction stage include product quality and reliability, promotion, and distribution.
Competition increases as the product moves through the stages of the product life cycle.
Marketing is important during all stages of the product life cycle to build awareness of the product and drive sales.
Product development is important during the introduction stage to refine the product and during the growth stage to meet the needs of the growing customers.
Distribution is important during all stages of the product life cycle to ensure that the product is readily available where and when customers want it.
Effective marketing strategies during the maturity stage include product differentiation, price competition, and promotion.


